
Rating scales as measures for clinical trials in neurology
The modified Ashworth Scale is designed to measure an individual's muscle tone, which is generally defined as the resistance of muscle as it is being passively lengthened or stretched and occurs as a result of the intrinsic synergies of muscle, tendon, and connective tissue as well as the active contraction of muscle (Blackburn, van Vliet.
Modified Ashworth Scale
The modified Ashworth scale is the most universally accepted clinical tool used to measure the increase of muscle tone. Spasticity was defined by Jim Lance in 1980, as a velocity-dependent increase in muscle stretch reflexes associated with increased muscle tone as a component of upper motor neuron syndrome. Spasticity has a wide range of.

Modified Ashworth Scale OT stuff Pinterest The o'jays
The Modified Ashworth Scale (MAS) is a measure of muscle spasticity. It was developed in 1982 by Dr Timothy A. Pedley and Dr David N. Simpson. The scale is used to rate the level of muscle tightness or spasm from 0 (no increase in muscle tone) to 4 (affected limb rigid in flexion or extension).
[PDF] Interrater reliability of a modified Ashworth scale of muscle
Patient Care Evidence-Based Practice Resources Tests and Measures Ashworth Scale (AS) and Modified Ashworth Scale (MAS) Ashworth Scale (AS) and Modified Ashworth Scale (MAS) Tests & Measures Summary What it measures: Both the Ashworth Scale (AS) and Modified Ashworth Scale (MAS) are used to assess spasticity. Target Population:

Definitions of the Modified Ashworth Scale and the Modified Modified
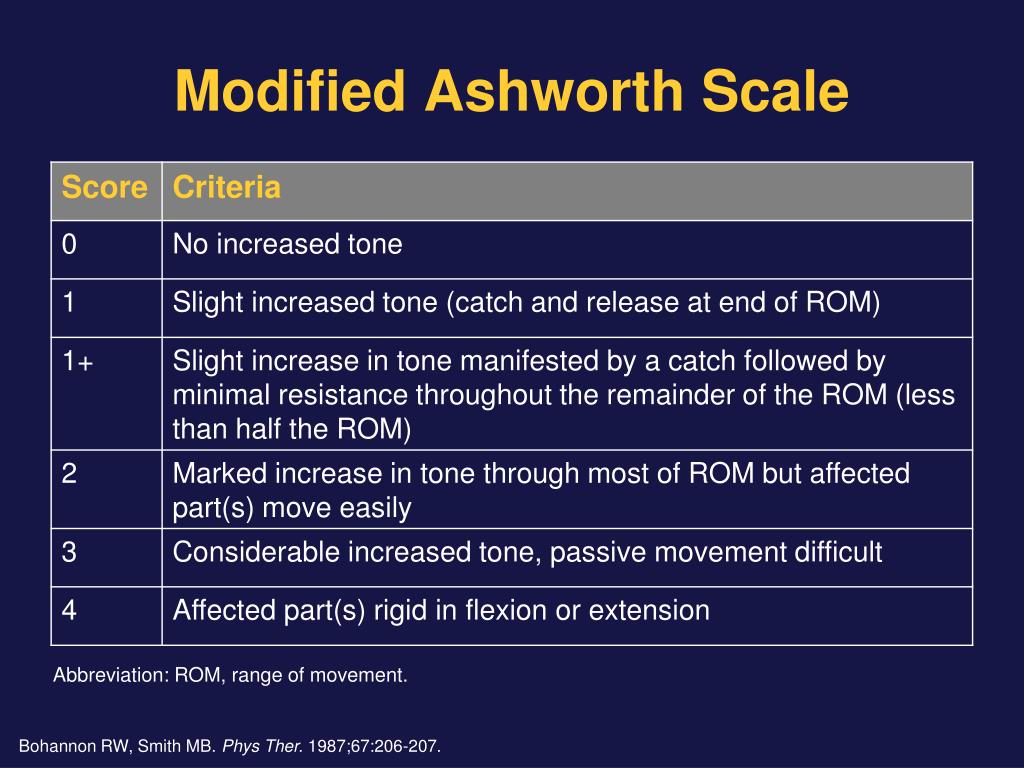
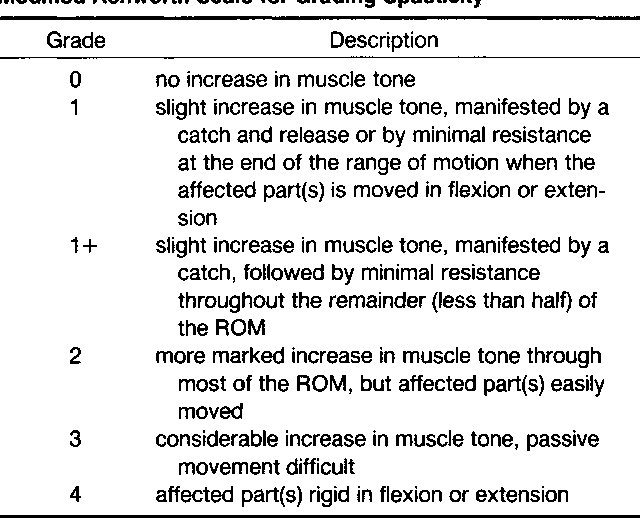
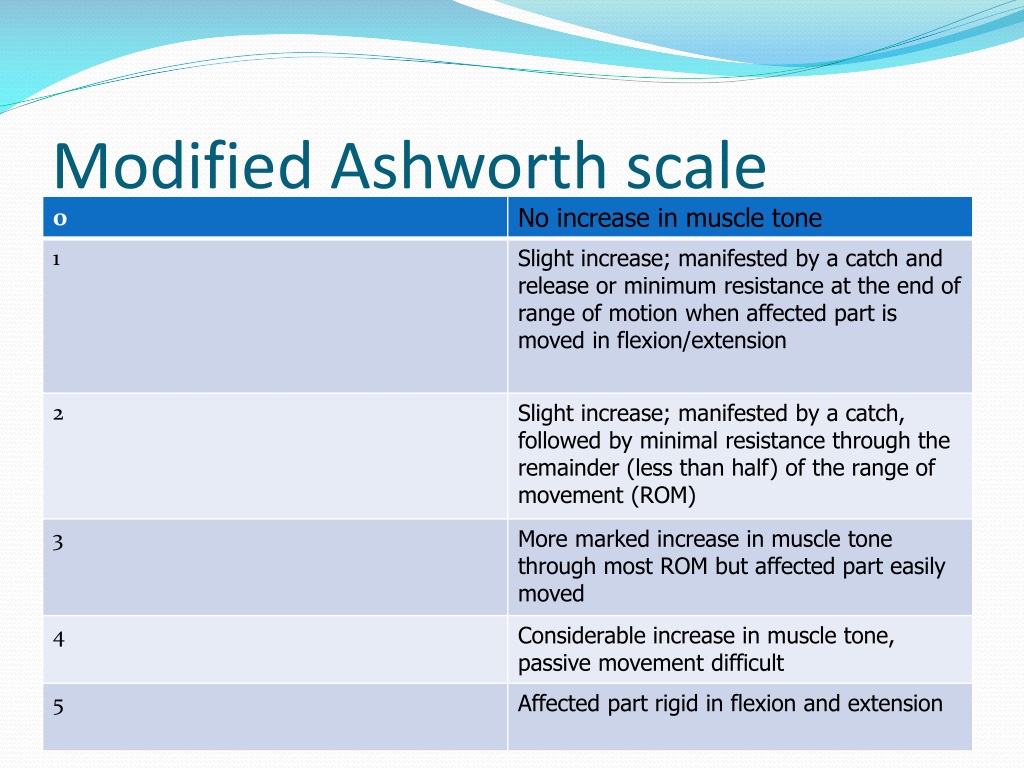
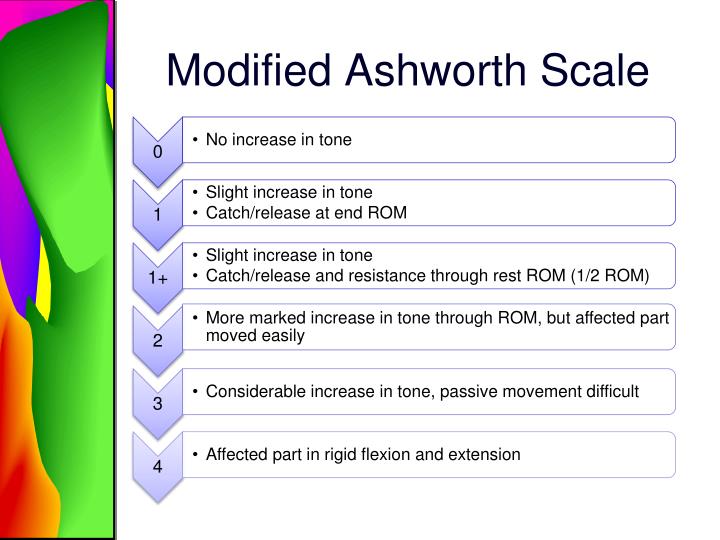
The modified Ashworth scale purpose is to grade muscle spasticity. The scale is as follows [4]: 0: No increase in muscle tone 1: Slight increase in muscle tone, with a catch and release or minimal resistance at the end of the range of motion when an affected part (s) is moved in flexion or extension

Muscle Tone Modified Ashworth Scale
Modified Ashworth Scale (MAS) is used to assess spasticity. [1] Intended Population Modified Ashworth Scale (MAS) have been utilized in the following populations: stroke, spinal cord injury, multiple sclerosis, cerebral palsy, traumatic brain injury, pediatric hypertonia and central nervous system lesions [2] Method of Use Description

MODIFIED ASHWORTH SCALE Review the MAS and original Ashworth Scale
The modified Ashworth scale is the most universally accepted clinical tool used to measure the increase of muscle tone. Spasticity was defined by Jim Lance in 1980, as a velocity-dependent increase in muscle stretch reflexes associated with increased muscle tone as a component of upper motor neuron.

A Review The Validity and Reliability of the Modified Ashworth Scale
Abstract Background: The Ashworth Scale and the modified Ashworth Scale are the primary clinical measures of spasticity. A prerequisite for using any scale is a knowledge of its characteristics and limitations, as these will play a part in analysing and interpreting the data.

Ashworth Scale /Modified Ashworth Scale (AS/MAS)
The Modified Ashworth Scale (MAS) is the most widely used clinical tool for the measurement of spasticity. However, its reliability has been questioned in some studies [4,5,6]. In children with spastic CP or hypertonia, the reliability of MAS varied across studies [7,8,9,10].
Modified Ashworth Scale Printable
The Modified Ashworth Scale (MAS) is a revised version of the original Ashworth Scale that measures spasticity in patients with lesions to the central nervous system. MAS is an assessment that is used to measure the increase in muscle tone. MAS assigns a grade of spasticity from a 0-4 ordinal scale.

Ashworth Scale /Modified Ashworth Scale (AS/MAS)
The modified Ashworth Scale is recommended to combine it with a quantitative measure of spasticity in every examination and be regarded as a measure of quality of movement, and standardization and re-examination of its reliability is particularly necessary. Introduction: The modified Ashworth Scale is the most commonly used measurement tool to evaluate spasticity in adults and CP-children.
Modified Ashworth Scale
PMID: 23166123 Comparing the validity of the Modified Modified Ashworth Scale (MMAS) and the Modified Tardieu Scale (MTS) in the assessment of wrist flexor spasticity in patients with stroke: protocol for a neurophysiological study

Modified Ashworth Scale Recovery Tech
The Modified Ashworth scale ( MAS) measures resistance during passive soft-tissue stretching and is used as a simple measure of spasticity. [1] Scoring (taken from Bohannon and Smith, 1987): 0: No increase in muscle tone

Modified Ashworth Scale YouTube
The Modified Ashworth Scale is a frequently used tool among Physiatrists, Neurologists, Physical therapists, and Occupational Therapists to classify the degree of spasticity and increased muscle tone in patients with upper motor neuron syndromes. It is commonly applied in patients with Stroke, Spinal Cord Injury and Traumatic Brain injury.

Modified Ashworth Scale 10 Download Table
The Modified Ashworth Scale is considered the primary clinical measure of muscle spasticity in patients with neurological conditions. However, some publications question its ability to measure spasticity

Modified Ashworth Scale The HKU Elearning Platform in Clinical
M o d i f i e d A s h wo r t h S c a l e ( M A S ) Grade Description 0 No increase in muscle tone 1 Slight increase in muscle tone, manifested by a catch