
Chapter 9 Anatomy & Physiology 181 with Torry at Illinois State
Regardless of its morphology or type, muscle tissue is composed of specialized cells known as muscle cells or myocytes (myo- [muscle, Greek = mys]), commonly referred to as muscle fibers (all of these terms are interchangeable); this is due to their extensive length and appearance. Myocytes are characterized by protein filaments known as actin and myosin that slide past one another, producing.

Các loại sơi cơ trong cơ thể mr vọc thể thao
Sliding filament model of muscle contraction Muscle contraction Neuromuscular junction and motor unit Osmosis Muscles high-yield notes offers clear overviews with striking illustrations, tables, and diagrams. Make learning more manageable.

SKELETAL MUSCLE PHYSIOLOGY STRUCTURE & TYPES OF MUSCLE FIBERS www
Fast-twitch, type II muscle fibers are further divided into type IIa and type IIb. Whereby type IIb (Fast-twitch glycolytic) fibers are more powerful but less resistant to fatigue than type IIa (Fast-twitch oxidative) fibers. For an image of muscle fibers from following paper: Muscle fiber type diversity revealed by anti‐myosin heavy chain.
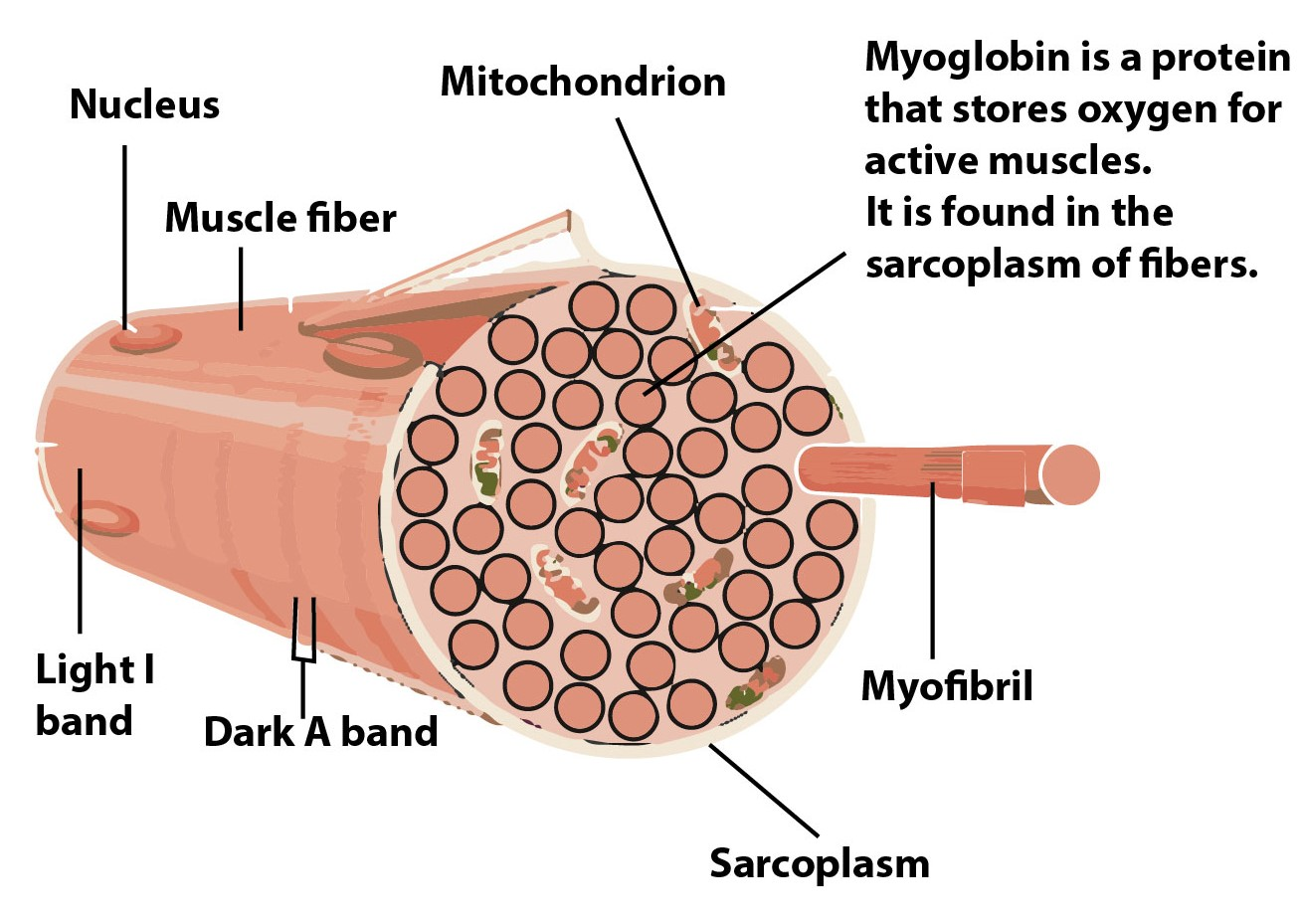
Define the following structure Muscle, Muscle fibre, Myofibril
Identify areas of the skeletal muscle fibers Describe excitation-contraction coupling The best-known feature of skeletal muscle is its ability to contract and cause movement. Skeletal muscles act not only to produce movement but also to stop movement, such as resisting gravity to maintain posture.
How Heat Affects Muscle Fibers in Meat ThermoWorks
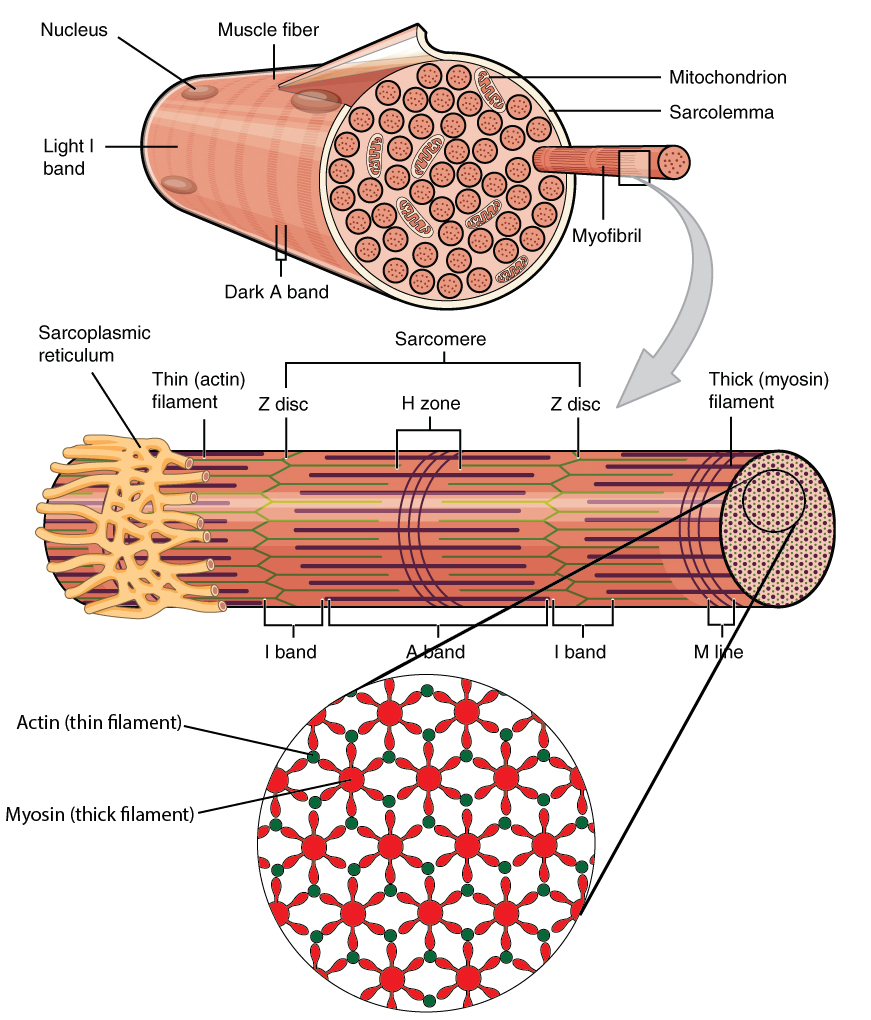
Muscle fibers are much longer than other cells as they were formed by many individual muscle cells fusing together when you were only an embryo. This makes the muscles strong, as any junctions between cells add a point of weakness.. Figure 3: A diagram of a section of a muscle fiber showing the intracellular structures of myofibrils, the.

39 diagram of muscle fiber Trailer Wiring Diagram
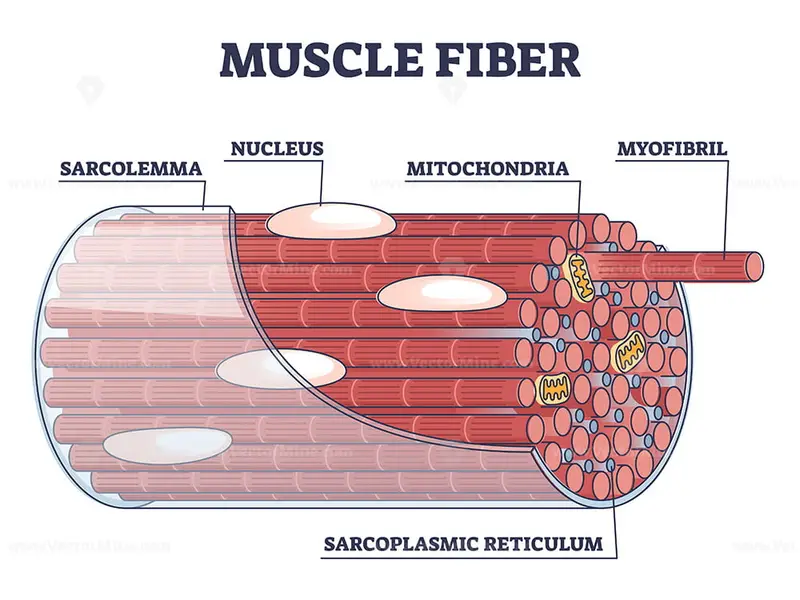
Diagram of the Structure of a Muscle Cell (also called a muscle fibre). The structure of a muscle cell can be explained using a diagram labelling muscle filaments, myofibrils, sarcoplasm, cell nuclei (nuclei is the plural word for the singular nucleus), sarcolemma, and the fascicle of which the muscle fibre is part. The structure of muscle fibers is included in courses in human biology and.

10.2 Skeletal Muscle Anatomy & Physiology
Diagram the process of cross-bridge cycling; The Neuromuscular Junction. The process of muscle contraction begins at the site where a motor neuron's terminal meets the muscle fiber—called the neuromuscular junction (NMJ). Every skeletal muscle fiber in every skeletal muscle is innervated by a motor neuron at a NMJ. Excitation signals from.

Structure of Muscle Fibers (IB Biology) YouTube
Muscles attach to bones directly or through tendons or aponeuroses. Skeletal muscles maintain posture, stabilize joints, support organs, control internal movement, and generate heat. Skeletal muscle fibers are long, multinucleated cells. The membrane of the cell is the sarcolemma; the cytoplasm of the cell is the sarcoplasm.
Muscle fiber structure and inner parts anatomical description outline
Skeletal Muscle Fibers Because skeletal muscle cells are long and cylindrical, they are commonly referred to as muscle fibers (or myofibers). Skeletal muscle fibers can be quite large compared to other cells, with diameters up to 100 μ m and lengths up to 30 cm (11.8 in) in the Sartorius of the upper leg.
Muscle Fiber Diagram Unlabeled , Free Transparent Clipart ClipartKey
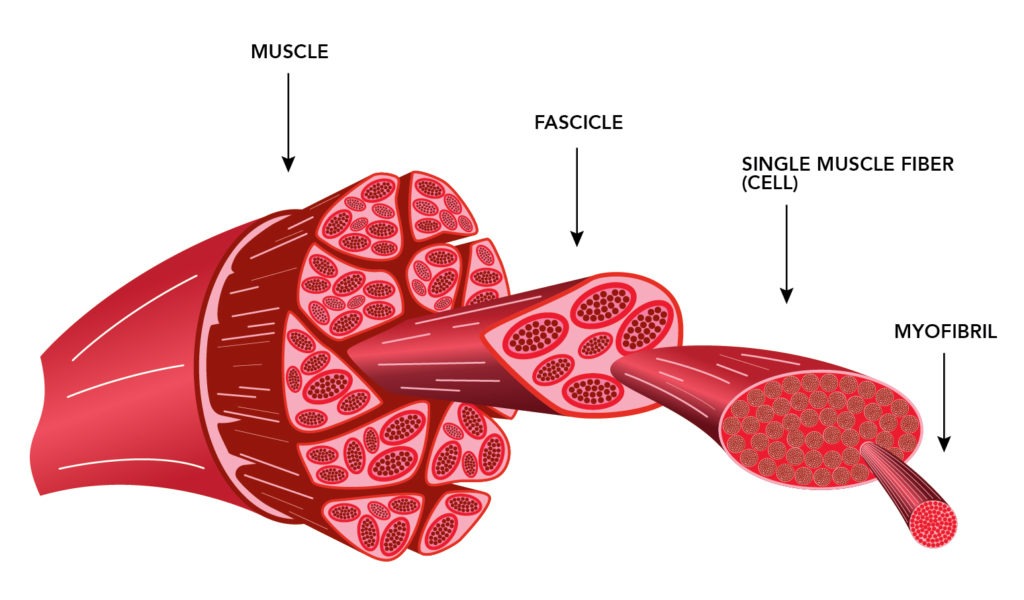
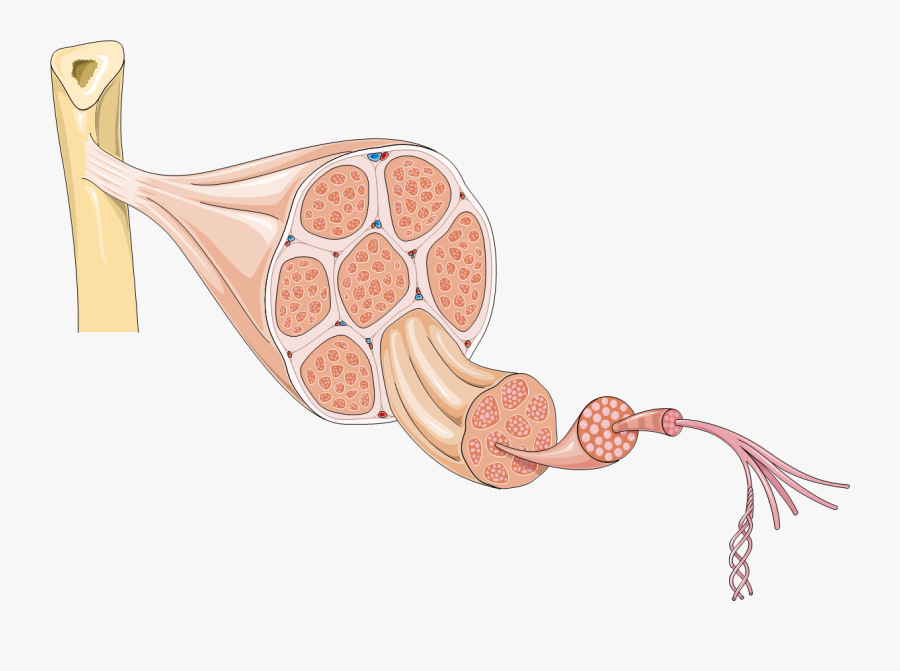
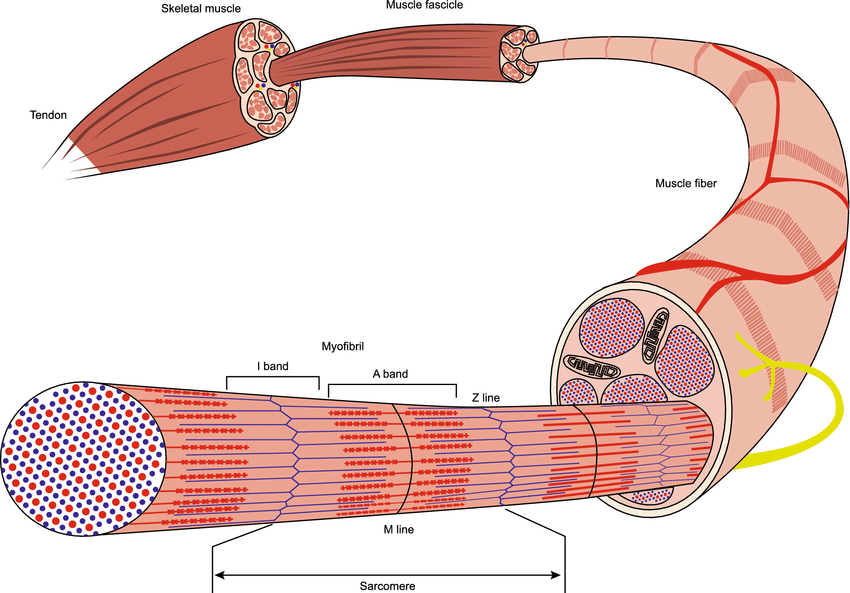
Figure 1. The Three Connective Tissue Layers. Bundles of muscle fibers, called fascicles, are covered by the perimysium. Muscle fibers are covered by the endomysium. Each skeletal muscle is an organ that consists of various integrated tissues. These tissues include the skeletal muscle fibers, blood vessels, nerve fibers, and connective tissue.
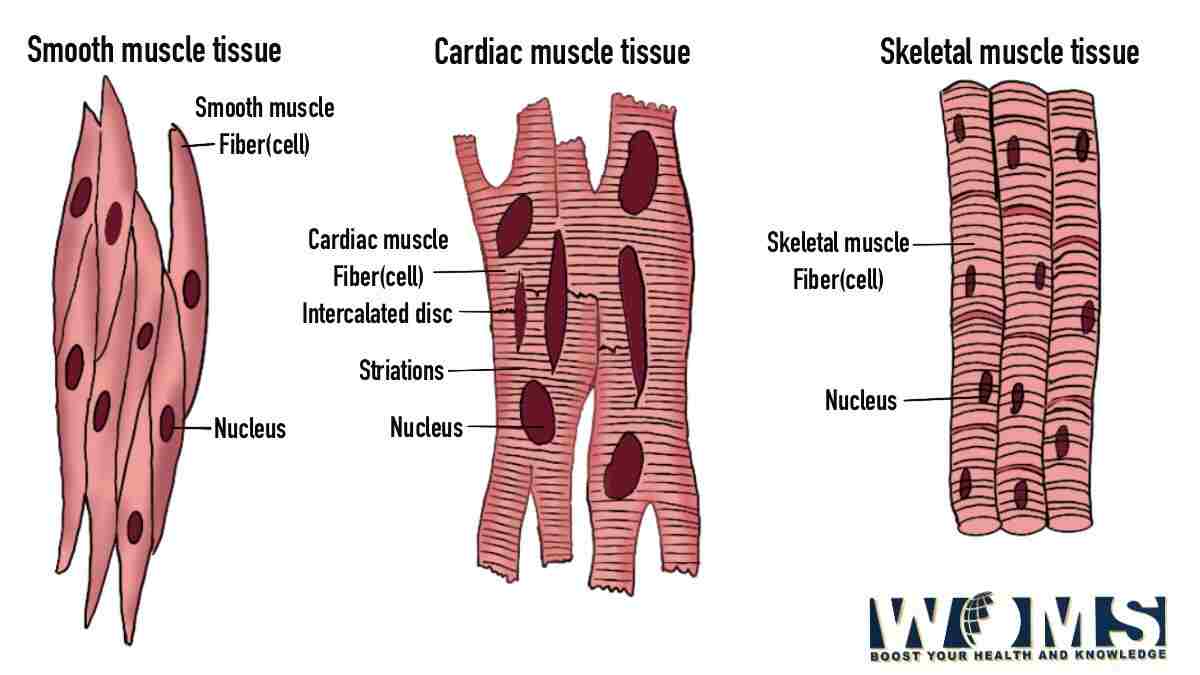
Diagram of Muscle Fiber 3 Types, Functions, and Anatomy WOMS
Describe the types of skeletal muscle fibers Explain fast and slow muscle fibers Two criteria to consider when classifying the types of muscle fibers are how fast some fibers contract relative to others, and how fibers produce ATP. Using these criteria, there are three main types of skeletal muscle fibers.
The structure of skeletal muscle. Striated muscle fiber consists of
An oxygen debt is created as a result of muscle use. The three types of muscle fiber are slow oxidative (SO), fast oxidative (FO) and fast glycolytic (FG). SO fibers use aerobic metabolism to produce low power contractions over long periods and are slow to fatigue. FO fibers use aerobic metabolism to produce ATP but produce higher tension.

Pin by Aline on Biology in 2022 Exercise physiology, Muscular system
The muscle fiber will repolarize, which closes the gates in the SR where Ca ++ was being released. ATP-driven pumps will move Ca ++ out of the sarcoplasm back into the SR. This results in the "reshielding" of the actin-binding sites on the thin filaments. Without the ability to form cross-bridges between the thin and thick filaments, the.

1000+ images about A&P.2.Skin.Bone.Muscle on Pinterest Models, Muscle
Skeletal muscle Each one of your skeletal muscles is made up of hundreds to thousands of muscle fibers that are tightly wrapped together by connective tissue. Each muscle fiber contains.

9.3 Skeletal muscle fibers contain calciumregulated molecular motors
The musculoskeletal system comprises one of the body's major tissue/organ systems. The three main types of muscle tissue are skeletal, cardiac, and smooth muscle groups. [1] [2] [3] Skeletal muscle attaches to the bone by tendons, and together they produce all body movements.
SKELETAL MUSCLE ORGANIZATION
Each bundle contains multiple muscle fibres, which are formed when individual muscle cells fuse together. Muscle fibres contain tubular myofibrils that run the length of the fibre and are responsible for muscular contraction. The myofibrils can be divided into repeating sections called sarcomeres, each of which represent a single contractile unit.